Raw material selection for cell therapy manufacturing can have a significant impact on the safety and efficacy of the final product. The input materials used in the manufacturing process can typically be classified into one of two categories:
- Raw materials – Materials used in manufacture of but not intended to be present in the final product – e.g., cell-culture media, growth factors, supplements, cytokines, cell-separation reagents. Also known as “ancillary materials” by US regulations.1
- Excipients – Materials administered as part of the product, help maintain quality attributes of the cells – e.g., electrolyte solutions, cryopreservatives.
As definitive regulations have not yet been developed for these materials, determining a qualification regime for the selection of raw materials (RMs) can be challenging and confusing for cell therapy manufacturers.
To clarify these issues, this blogpost intends to provide a high-level overview of the considerations used to select raw materials that mitigate risk and align with current regulatory guidelines.
For more information, check out the accompanying chapter on raw material considerations (chapter 1) in our Cell Therapy Handbook.
What Type of Qualification is Required for Ancillary Materials?
To date, no specific cGMP guidance exists for raw material manufacturing2—suppliers may say their products are manufactured under cGMP conditions, with claims ranging from declarations of cGMP based on following a subset of cGMP guidelines; independent quality management system certification (e.g., ISO9001); or even regulatory agency inspection if the site is manufacturing regulated products.
One of the most globally recognized raw material guidance documents, USP <1043>, provides a framework for classifying raw materials into four different tiers based on risk.
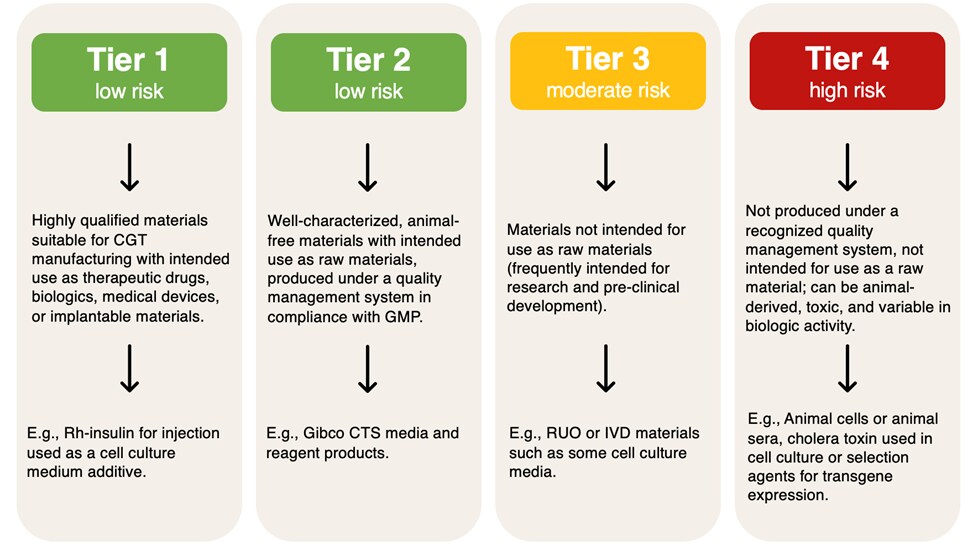
Figure 1. USP <1043> raw material risk categories
Summary
A cell therapy’s manufacturing components are critical to developing a reproducible and safe product. Proper sourcing of materials early in development of a cell therapy from reliable suppliers who make products specifically for cell therapeutics can shorten the development timeline, dramatically reduce costs, and improve the likelihood of approval from regulatory authorities.
Additional resources
This article provides an overview of the numerous challenges and considerations that a cell therapy manufacturer must address while selecting appropriate raw materials. For more in-depth discussions on these topics, we recommend reading up on the accompanying chapter in our Cell Therapy Handbook.
References
- Thermo Fisher Scientific (2020) Manufacturing pluripotent cell therapeutics
- USP (2006) General Chapter <1043>: Ancillary Materials for Cell- and Tissue-Based Products. In: USP-NF English Edition. Rockville: United States Pharmacopeial Convention.