Authors: Aparna Chandrasekaran and Cameron Smurthwaite
Cellular constituents elements are organized into membrane-bound and non-membrane bound compartments called ‘Organelles’. These structurally complex compartments carry out specific biological functions which are determined by the distinct enzymes/proteins they contain. These unique proteins can aid in the study of the morphology and function of the cell and its organelles.
Spatial-temporal mapping and characterization of the protein of interest are essential in interpreting its subcellular location and its role in different cellular mechanisms and functions. Although mass spectrometry and gel-based electrophoresis approaches have been at the forefront of high throughput techniques for proteome analysis, imaging-based techniques have enabled scientists to visualize the proteins in situ in individual cells at a high resolution.
Antibodies as cell and organelle markers
One approach for imaging-based techniques involves co-localization with antibodies that target proteins within a specific organelle called organelle markers to accurately identify the spatial distribution and potential function of the protein of interest within the cell. Co-localization studies using antibodies that demonstrate relationships between different proteins can also aid in visualizing multiple organelles simultaneously by using organelle marker antibodies of different isotypes or from different host species. These markers serve as essential tools in western blot assays to confirm the organelle-specific fractionation of cell lysates. The versatile range of fluorescent colors available for the organelle stains accommodates for co-staining experiments with organelle-specific antibodies to monitor cellular movement and location.
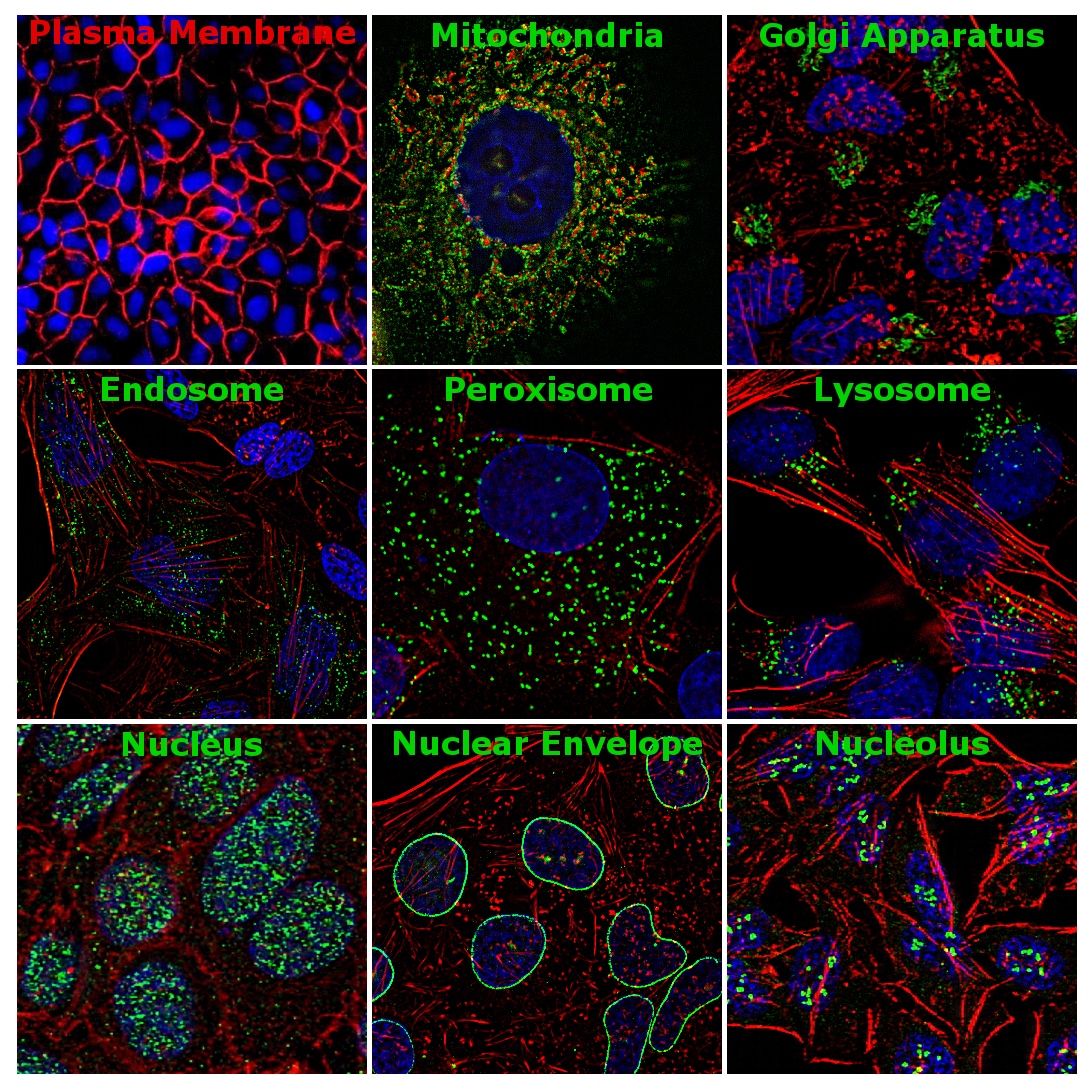
Figure 1 | Immunofluorescence analysis of antibody markers staining different subcellular components. Plasma membrane – Pan-cadherin Polyclonal Antibody (Cat. No. 71-7100), mitochondria – HK1 Recombinant Polyclonal Antibody (Cat. No. 711777), Golgi apparatus – GM130 Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (10H5L5) (Cat. No. 703794) peroxisome – Catalase Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (10H47L17) (Cat. No. 702955), lysosome – LIMP2 Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal (22H6L14) (Cat. No. 703037), endosome – Caveolin 1 Polyclonal Antibody (Cat. No. PA5-17447), nucleus – LSD Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (3H8L63) (Cat. No.703761), nuclear envelope – Lamin B1 Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (10H34L18) (Cat. No. 702972) and nucleolus – Fibrillarin Monoclonal Antibody (38F3) (Cat. No. 480009).
Invitrogen offers antibodies against organelle-specific proteins that have been validated for use in various applications such as ELISA, western blot, flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, and immunoprecipitation. Key organelle marker targets are summarized in Table 1. Invitrogen antibodies undergo rigorous two-part testing to validate their performance based on sensitivity, specificity and functionality.
Table 1 | Invitrogen antibodies as organelle markers
|
S. No |
Organelle |
Protein |
Catalog # |
Product Description |
|
1 |
Cell Junctions |
ZO-3 |
701825 |
|
|
2 |
Plasma Membrane |
Pan-Cadherin |
71-7100 |
|
|
3 |
Mitochondria |
Hexokinase 1 |
711777 |
|
|
4 |
Golgi Apparatus |
GM130 |
703794 |
|
|
5 |
Endoplasmic reticulum |
Calnexin |
PA5-34754 |
|
|
6 |
Cytoskeleton |
Vimentin |
MA1-10459 |
|
|
7 |
Peroxisome |
Catalase |
702955 |
|
|
8 |
Lysosome |
LIMP2 |
703037 |
|
|
9 |
Proteasome |
PSMA3 |
703791 |
|
|
10 |
Ribosome |
RPS6 |
710405 |
|
|
11 |
Endosome |
Caveolin 1 |
PA5-17447 |
|
|
12 |
Autophagosome |
ATG12 |
701684 |
|
|
13 |
Nucleus |
LSD1 |
703761 |
|
|
14 |
Nuclear Envelope |
Lamin B1 |
702972 |
|
|
15 |
Nucleolus |
Fibrillarin |
480009 |
Fluorescent Dyes as cell and organelle markers
Conventional imaging-based approaches utilizes fluorescent dyes as counterstains to identify the subcellular location of a specific protein. Invitrogen offers a versatile range of organelle-specific dyes and stains that are represented in Table 12 for multiplex analysis in live cells or fixed-cells for imaging.
Products listed come with many different fluorescence readouts ranging across the visible spectrum, allowing for multiplexing your imaging experiments with other organelle stains or fluorescently conjugated antibodies.
Table 2 | Organelle dyes for fixed and live cell imaging
|
S. No |
Organelle |
Product Description |
Catalog # |
|
1 |
Cell Tracking |
CellTracker |
|
|
2 |
Plasma Membrane |
CellLight Plasma Membrane, CellMask Plasma Membrane, Wheat Germ Agglutinin Alexa Fluor™ conjugates |
|
|
3 |
Mitochondria |
CellLight Mitochondria, MitoTracker |
|
|
4 |
Golgi Apparatus |
CellLight Golgi |
|
|
5 |
Endoplasmic reticulum |
CellLight ER |
|
|
6 |
Cytoskeleton |
CellLight Actin, CellLight Tubulin, CellMask, Alexa Fluor Phalloidin conjugates, ReadyProbes Reagent |
A22281, R37110, A57243, R37112, C10503, A12381, A30105, A57245 |
|
7 |
Peroxisome |
CellLight Peroxisome |
|
|
8 |
Lysosome |
CellLight Lysosome |
|
|
9 |
Nucleus |
CellLight Nucleus, HCS NuclearMask, SYTO, SYTOX, Hoechst |
S11368, H21486, H10325, S7020, C10602, S11363, H10326, T3605, S34901 |
*For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Additional Antibody Blogs
Let’s get ‘specific’ about the TNFR pathway!
DIY Neurons for antibody validation
Translate to Invitrogen antibodies for your ribosomal protein research!
Drivers of the Chromosomal Passenger Complex
PRMTs: Role in epigenetic regulation
Using Blockers to Unlock Secretory Proteins
Specific and neutralizing recombinant antibodies to SARS-CoV-2
About
<Endoplasmic reticulum
CellLight ER
C10590, C10591>
C10591imaging RED ;This is stain the few parts of helacellER
Not all cells
but
C10590 Imaging Green All Helacells ER are stained by this .
What each cause?