Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
Trimethylsilyl cyanide, 97%, Thermo Scientific Chemicals
Catalog number A19598.06
also known as A19598-06
Price (USD)/ Each
48.65
Special Offer
Online exclusive
Ends: 31-Dec-2024
56.80 Save 8.15 (14%)
-
Quantity:
5 g
Price (USD)/ Each
48.65
Special Offer
Online exclusive
Ends: 31-Dec-2024
56.80 Save 8.15 (14%)
Trimethylsilyl cyanide, 97%, Thermo Scientific Chemicals
Catalog numberA19598.06
Price (USD)/ Each
48.65
Special Offer
Online exclusive
Ends: 31-Dec-2024
56.80 Save 8.15 (14%)
-
Chemical Identifiers
CAS7677-24-9
IUPAC Nametrimethylsilanecarbonitrile
Molecular FormulaC4H9NSi
InChI KeyLEIMLDGFXIOXMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
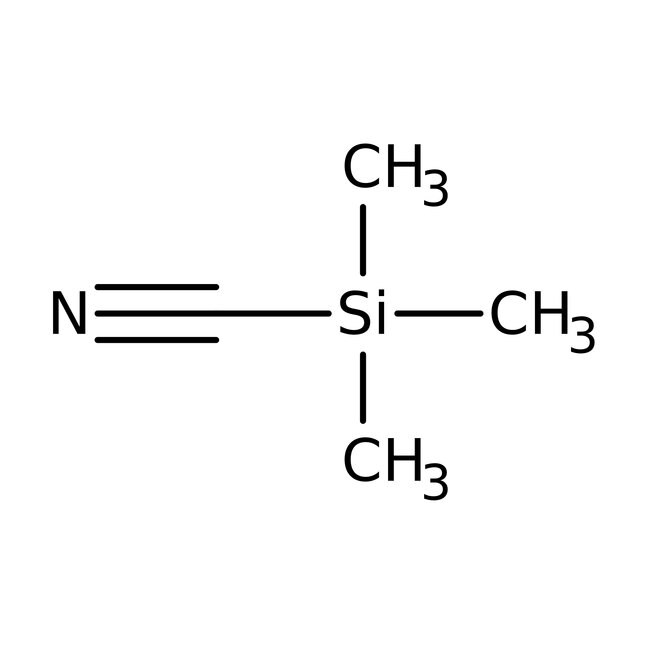
SMILESC[Si](C)(C)C#N
View more
Specifications Specification Sheet
Specification Sheet
Assay (GC)≥96.0% (non-U.S. sourced material)
Appearance (Color)Clear, colorless to yellow
Assay from Supplier's CofA≥96.0% (U.S. sourced material)
CommentRI ca 1.3910 (non-U.S. sourced material)
FormLiquid
View more
Trimethylsilyl Cyanide is used as a reagent in the preparation of optically active cyanohydrins. It is used in the derivatization of complex metabolite mixtures by GC-MS. It is employed in the preparation of Reissert compounds, which represent reactive polyamides. Further, it is used to convert pyridine-N-oxides into 2-cyanopyridine. It is also used as a cyanide source in an enantioselective organocatalytic Strecker-type reaction of aliphatic N,N-dialkylhydrazones. In addition to this, it is used as a reagent for the cyanosilylation of aldehydes.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
Trimethylsilyl Cyanide is used as a reagent in the preparation of optically active cyanohydrins. It is used in the derivatization of complex metabolite mixtures by GC-MS. It is employed in the preparation of Reissert compounds, which represent reactive polyamides. Further, it is used to convert pyridine-N-oxides into 2-cyanopyridine. It is also used as a cyanide source in an enantioselective organocatalytic Strecker-type reaction of aliphatic N,N-dialkylhydrazones. In addition to this, it is used as a reagent for the cyanosilylation of aldehydes.
Solubility
Miscible with organic solvents.
Notes
Moisture sensitive. Store in a cool place.Incompatible with water, strong oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents, strong acids and strong bases.
Trimethylsilyl Cyanide is used as a reagent in the preparation of optically active cyanohydrins. It is used in the derivatization of complex metabolite mixtures by GC-MS. It is employed in the preparation of Reissert compounds, which represent reactive polyamides. Further, it is used to convert pyridine-N-oxides into 2-cyanopyridine. It is also used as a cyanide source in an enantioselective organocatalytic Strecker-type reaction of aliphatic N,N-dialkylhydrazones. In addition to this, it is used as a reagent for the cyanosilylation of aldehydes.
Solubility
Miscible with organic solvents.
Notes
Moisture sensitive. Store in a cool place.Incompatible with water, strong oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents, strong acids and strong bases.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Reagent for the formation of O-TMS cyanohydrins from carbonyl compounds.
- The ZnI2-catalyzed procedure allows cyanohydrins of unreactive ketones to be prepared in good yield, avoiding the unfavourable equilibria often encountered with the classical alkali cyanide method. For details and list of examples, see: Org. Synth. Coll., 7, 20 (1990). Other catalysts including Et3N or Bu3P are also effective: Chem. Lett., 537, 541 (1991). For catalysis by Methyl triphenyl phosphonium iodide, A15644 , see: Tetrahedron Lett., 44, 6157 (2003). In the absence of a catalyst, aldehydes have been found to give good yields of the TMS cyanohydrin, but reaction with ketones is very slow: J. Chem. Soc., Perkin 1, 2383 (1995). For use of Tetracyanoethyl ene, A13945 , as a ã-acid catalyst for both aldehydes and ketones, see: J. Chem. Soc., Perkin 1, 2155 (1995). Under the same conditions, dimethyl acetals give O-methyl cyanohydrins.
- For examples of transformations of ketone TMS cyanohydrins, see: Chem. Pharm. Bull., 43, 1294 (1995).
- For use in asymmetric Strecker synthesis of chiral amino acids, see: Tetrahedron Lett., 29, 4397 (1988).
- Tertiary alkyl halides normally undergo elimination when treated with alkali cyanides, but can be converted to the corresponding nitriles by reaction with TMSCN in the presence of SnCl4: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 20, 117 (1981).
- Reacts with epoxides in the presence of ZnI2 to give trans-ɑ-siloxy isocyanides, which can be readily hydrolyzed to the hydroxy isocyanides: J. Am. Chem. Soc., 104, 5849 (1982); Org. Synth. Coll., 7, 294 (1990). In the presence of Ag salts (AgClO4, AgBF4 or AgOTf), alkenes can be converted to isocyanides in Markovnikov fashion: Synlett, 288 (1999).
- For a brief survey of uses of this reagent in synthesis, see: Synlett, 1625 (2007).